Laptops
Laptops have become essential tools for work, education, and entertainment. With their portability, versatility, and power, they are indispensable for professionals, students, and gamers alike. In this blog, we explore the history of laptops, their key features, the different types available, and future technological trends.
The Evolution of Laptops
The development of laptops is a fascinating journey of technological advancements aimed at increasing portability without compromising power:

The Beginnings (1980s): The first laptops, like the Osborne 1 and the IBM 5155, were bulky and had limited processing power. They were designed primarily for business use, offering basic word processing and spreadsheet capabilities.

The 1990s: This decade saw significant improvements in laptop design, with the introduction of thinner and lighter models like the IBM ThinkPad and Apple PowerBook. Laptops began to feature color displays, trackpads, and more powerful processors.
The 2000s: Laptops became more mainstream, with models like the Dell Inspiron and Apple MacBook gaining popularity. This era saw the introduction of Wi-Fi connectivity, built-in webcams, and longer battery life.
The 2010s: The introduction of ultrabooks, pioneered by the MacBook Air, brought even thinner and lighter laptops with solid-state drives (SSDs) for faster performance. Touchscreens, convertible designs, and high-resolution displays became common.
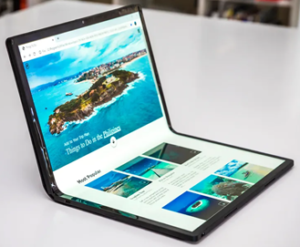
The 2020s and Beyond: Modern laptops are powerful enough to replace desktops for many tasks. They feature advanced processors, high-definition displays, and long-lasting batteries. Innovations like foldable screens like Intel’s Horseshoe bend, 2-in-1 designs, and AI-driven features are shaping the future of laptops.
Key Features of Modern Laptops
Today’s laptops are packed with features that cater to various needs, from basic tasks to demanding professional work. Here are some of the most important features:
Processors (CPUs): The processor (central processing unit) is the heart of the laptop, determining the overall performance. Intel’s Core series (i3, i5, i7 and i9) and AMD’s Rayzen series are popular choices, with higher numbers indicating better performance. For lightweight tasks, an i3 or Ryzen 3 is sufficient, while i7 or Ryzen 7 is better for heavy multitasking and gaming. New processors like Apple’s M1, M2 and M3 series processors are powerful and power efficient.
Memory (RAM): RAM (Random Access Memory) is crucial for multitasking and running applications smoothly. Most modern laptops come with 8GB or 16GB of RAM, with 32GB or more available for high-performance laptops. More RAM allows for better performance when running multiple applications simultaneously.
Storage: Laptops typically come with SSDs (Solid State Drives) or HDDs (Hard Disk Drives). SSDs are faster, more reliable, and quieter than HDDs, making them the preferred choice. Common storage capacities range from 256 GB to 1 TB or more. Some laptops also offer hybrid storage solutions, combining SSDs for speed with HDDs for additional capacity.
Graphics (GPU): Graphics, or GPU (Graphics Processing Unit) comes in two forms: integrated graphics is built into the CPU and it is sufficient for basic tasks like web browsing and video streaming. and dedicated GPUs, like NVIDIA’s GeForce or AMD’s Radeon, are necessary for gaming, video editing, and 3D modeling.
Display: Laptop displays vary in size and resolution. Common sizes range from 13 to 17 inches, with resolutions from Full HD (1920×1080) to 4K (3840×2160). High-resolution displays offer sharper images, while touchscreens and 2-in-1 designs add versatility.
Battery Life: Battery life is a critical factor for portability. Laptops with energy-efficient processors and displays can last up to 10 hours or more on a single charge. However, high-performance laptops, especially gaming models, may have shorter battery life.
Operating System (OS): The choice of operating system is a significant factor when selecting a laptop. Windows, macOS, and Linux are the most common options:
Windows: is the most popular OS, known for its versatility and compatibility with a wide range of software. It’s suitable for everything from gaming to professional work.
macOS: Exclusive to Apple’s MacBook lineup, macOS is known for its smooth user experience, seamless integration with other Apple devices, and reliability.
Linux: is an open-source OS preferred by developers and tech enthusiasts for its flexibility and customization options.
Connectivity: Modern laptops come with various connectivity options, including an Ethernet connection port (RJ-45), universal serial bus (USB) ports, 3.5 mm audio jack, high-definition multimedia interface (HDMI), SD card reader, video graphics array (VGA) port, Bluetooth, and Wi-Fi 6. Some models also offer Thunderbolt ports for faster data transfer and connection to external GPUs and displays.
Build Quality and Design: Laptops are available in various materials, from plastic to aluminum and carbon fiber. Ultrabook laptops prioritize thin and light designs, while gaming laptops are often bulkier with enhanced cooling systems.
Types of Laptops
There are several types of laptops, each catering to different needs and use cases:
Ultrabooks: Ultrabooks are slim, lightweight laptops designed for portability and efficiency. They typically feature long battery life, SSD storage, and high-resolution displays. Ultrabooks are ideal for professionals and students who need a portable yet powerful device for everyday tasks.
Gaming Laptops: Gaming laptops are built for performance, featuring powerful processors, dedicated GPUs, and high-refresh-rate displays. They are often bulkier and have advanced cooling systems to handle intense gaming sessions. These laptops are also suitable for video editing and 3D rendering.
2-in-1 Laptops (Convertible/Hybrid): These laptops can function as both a laptop and a tablet, thanks to a touchscreen and a flexible hinge that allows the screen to be flipped or detached. They are versatile and suitable for users who need both productivity and entertainment in one device.
Business Laptops: Business laptops prioritize durability, security, and productivity features. They often come with enterprise-level security options, longer battery life, and comfortable keyboards. Examples include the Lenovo ThinkPad and Dell Latitude series.
Budget Laptops: These laptops offer basic functionality at an affordable price. They are suitable for students or casual users who need a device for web browsing, word processing, and media consumption. Budget laptops often have lower specs but are more than adequate for everyday tasks.
Workstations: Mobile workstations are high-performance laptops designed for professional work that requires powerful processing, such as computer-aided design (CAD), 3D rendering, and scientific simulations. They come with advanced CPUs, GPUs, and large amounts of RAM and storage.
Netbooks/Chromebooks: These are ultra-portable and affordable laptops primarily designed for internet-based tasks. Chromebooks run on Google’s Chrome OS and are ideal for students and users who rely on cloud-based applications.
Future Trends in Laptop Technology
The laptop industry continues to evolve, with several trends shaping the future:
AI Integration: AI (artificial intelligence) is being integrated into laptops for tasks like predictive typing, battery optimization, and enhancing the user experience. Expect smarter and more intuitive devices in the future.
Foldable and Dual-Screen Laptops: Innovative designs like foldable screens and dual-screen laptops are emerging, offering new ways to interact with devices and multitask.
Improved Battery Technology: Advances in battery technology will lead to even longer battery life, enabling laptops to last all day on a single charge, even with intensive use.
Sustainable and Eco-Friendly Laptops: As environmental concerns grow, manufacturers are focusing on sustainability, using recycled materials, and reducing e-waste by offering modular designs and longer software support.
5G Connectivity: With the rollout of 5G networks, laptops with built-in 5G modems will become more common, providing faster and more reliable internet connections, especially for mobile workers.
Laptops have come a long way from their early days as bulky, business-focused machines. Today, they are versatile tools that cater to a wide range of needs, from basic computing to high-performance tasks. Whether you’re a student, professional, gamer, or casual user, there’s a laptop out there that’s perfect for you. By understanding the key features and types of laptops, you can make an informed decision and choose a device that will serve you well for years to come.
